Joplin Plugin - Dungeons and Dragons Character Manager
Published:
A Joplin plugin to manage Dungeons & Dragons 5e characters directly in your notes.
Published:
A Joplin plugin to manage Dungeons & Dragons 5e characters directly in your notes.
Published:
An open-source chess analysis tool, in the form of a python package. Check it out!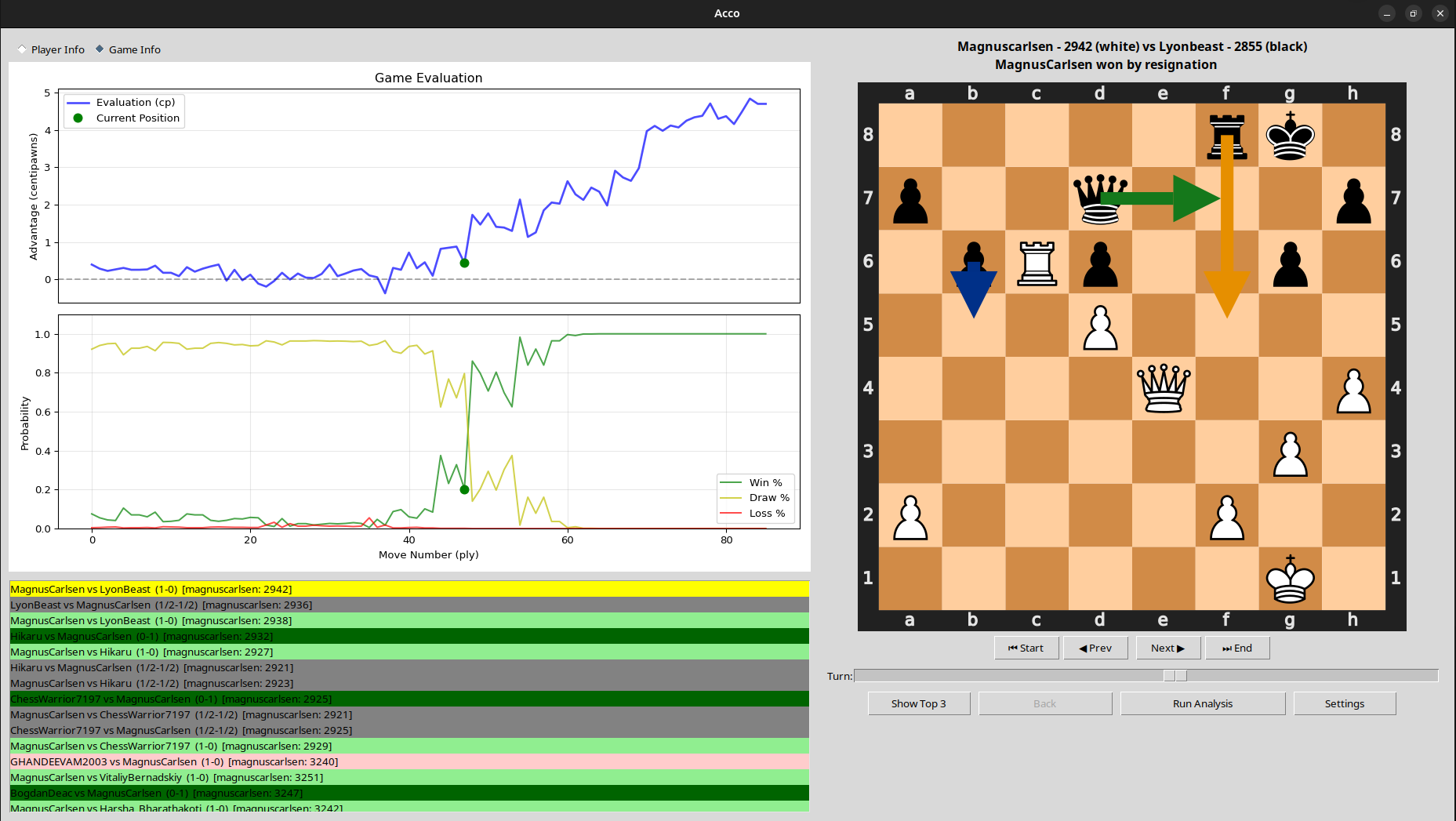
Published:
This was a project for EEL 5934: Autonomous Robotics, taken at the University of Florida with Dr. Islam 
Published:
We trained 5 classifiers for 5 types of cancer as a final project for a graduate Computer Vision course.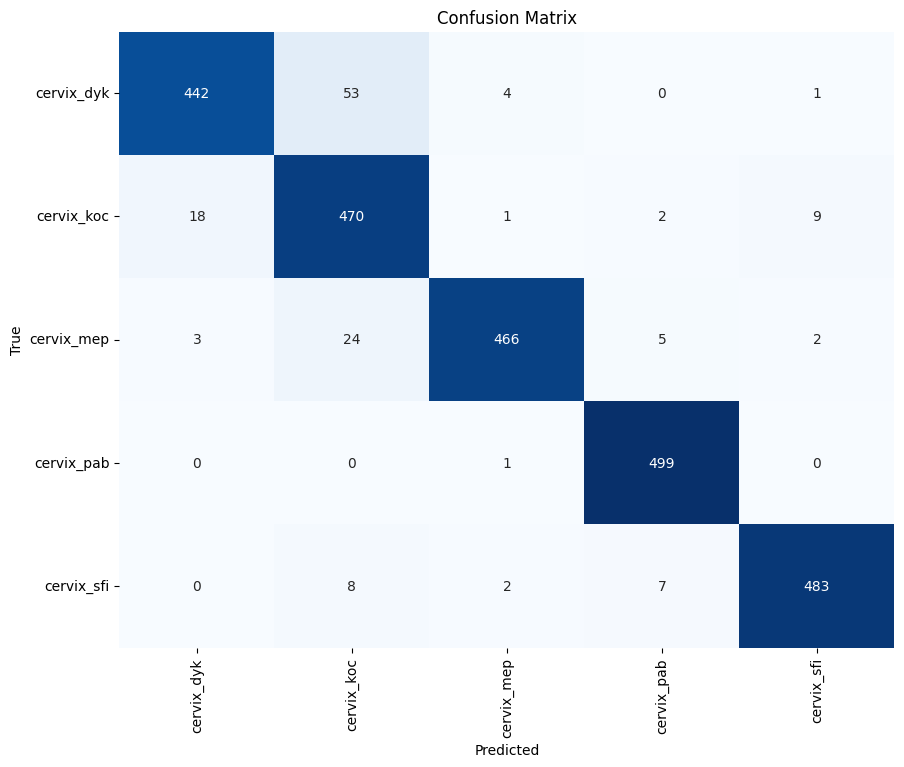
Published:
A collaborative simulation of possible technologies to establish a permanent presence in our solar neighborhood
Published in ICAA, 2024
The NeSy Program Synthesis approach is evaluated using 600 multi- hop navigation tasks with 1 to 10 hops. Compared with neural approaches, the our approach improves the success rate and path efficiency by an average of 64.3% and 19.4% across all tasks, respectively.
Recommended citation: William English, Dominic Simon, M. R. Ahmed, Sumit Jha, and Rickard Ewetz, “Neuro-Symbolic Program Synthesis for Multi-Hop Natural Language Navigation”, International Conference on Assured Autonomy (ICAA), 2024.
Published in ICMLA, 2024
NSP uses a feedback loop from the symbolic execution environment to the neural generation process to self-correct syntax errors and satisfy execution time constraints. We evaluate our neuro-symbolic approach using a benchmark suite with 1500 path-planning problems. The experimental evaluation shows that our neuro-symbolic approach produces 90.1% valid paths that are on average 19-77% shorter than state-of-the-art neural approaches.
Recommended citation: William English, Dominic Simon, Sumit Jha, and Rickard Ewetz, “NSP: A Neuro-Symbolic Natural Language Navigational Planner”, International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), 2024. https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.06859
Published in ICML, 2025
In this paper, we propose a framework for NL to TL translation called Grammar Forced Translation (GraFT). The framework is based on the observation that previous work solves both the grounding and translation steps by letting a language model iteratively predict tokens from its full vocabulary. GraFT reduces the complexity of both tasks by restricting the set of valid output tokens from the full vocabulary to only a handful in each step. Compared with state-of-the-art translation approaches, it can be observed that GraFT improves the end-to-end translation accuracy by 5.49% and out-of-domain translation accuracy by 14.06% on average.
Recommended citation: William English, Dominic Simon, Sumit Jha, and Rickard Ewetz, “Grammar-Forced Translation of Natural Language to Temporal Logic using LLMs”, International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2025. https://icml.cc/virtual/2025/poster/44027
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.